Hair Transplant Methods
Somewhat dubious though it may seem, yet the first known baldness treatment returns to 3500 years ago, showing the significance of the problem. Statistics suggest that the number of hair transplants is rising by 20% annually. This is due to the increasing demands for an attractive appearance and resolving undesirable social and psychological consequences of going bald, especially in today’s world. Thanks to cutting-edge technology that have evolved to impressive heights, today, the operation to transplant hair has become more convenient to patients. Moreover, the results imitate the way hair grows naturally and is undetectable as a hair transplant. Therefore, the procedure is now fairly common particularly to treat male pattern baldness. Other hairless areas such as the eyebrows, eyelashes, beard, mustache, and chest can also be restored by this procedure, and likewise bald injury scars and some women’s issues.
History
The use of grafts in hair transplantation goes back to the nineteenth century. In 1930, Japanese surgeons used follicular unit grafts to restore eyelashes and eyebrows. Dermatologist Norman Orentreich treated hairless areas of the scalp by using free donor grafts in the late 1950s. Follicular unit extraction was first described by Masumi Inaba in Japan in 1988. Today, the procedure has dominated the field of hair transplants since it was introduced on a global scale in 2003.
What is hair transplantation?
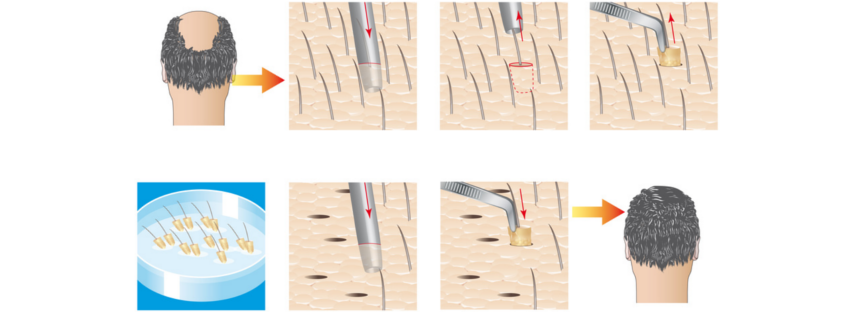
Hair transplantation is a surgical procedure surgeons utilize to dislodge hair follicles from a donor site of the body to a bald recipient cite. For example, the hair follicles of the back of the head are transplanted to the hairless areas of the scalp. Appropriate extraction of the hair follicle is crucial to guarantee the viability of the hair and avoid the cutting of the hair shaft from the hair follicle. The surgery is conducted under local anesthesia and on an outpatient basis. During the first ten days most of the transplanted hairs will fall out, but after about three months new hair will grow. Among the several various techniques, there are two main methods for extracting donor grafts: strip excision harvesting (FUT-strip) and follicular unit extraction (FUE). There are also some innovative devices such as Robotic Hair Restoration where a robot helps the surgeon to identify suitable follicles and extract them individually at a rate of up to 1000 per hour. However, the device has some disadvantages such as making large holes in the scalp and high cost.
FUT-strip technique
In FUT-strip procedure, the surgeon picks up a strip of hair-rich skin (about 1.5 x 22 cm) from the back of the head. Then the follicles are separated carefully from the strip by a skilled clinical team and placed into the tiny punctures or incisions made in the bald areas of the scalp in a predetermined form. In FUT-strip, stereo-microscopic separation permits each follicular units to be removed from the strip without being damaged. This technique allows for the greatest number of follicles to be transplanted in a single operation. The main disadvantage of this technique is leaving a linear scar in the donor site. The patient may have chronic pain and hyperesthesia in the scar. The risk of damaging the follicles is higher than FUE method. Recently, there has been a withdrawn of this technique as the FUE technique develops.
FUE technique
Today, state-of-the-art follicular unit extraction method has become the preferred choice of treatment for most baldness cases. In this minimally-invasive procedure, the follicles units containing several hairs are removed in a random way and there is less density in the donor area. The follicles are removed by using micro-sized punches and placed into the tiny holes or incisions made in the scalp recipient site in a consistent style. Typically, FUE procedures last according to the treatment plan and obviously more than strip surgeries; therefore, grafts remain longer out of the body, risking sub-optimal growth. The main advantage of this technique over FUT-strip is that in FUE, there is no need for harvesting large areas of the scalp. Consequently, there will be no major scar on the head and the risk of infection is minimized. Moreover, there is no need for sutures and the pain and discomfort following the surgery are much less than FUT-strip. In addition, the recovery time is about a week, half that of FUT-strip. In FUE the operation traces are undetectable and the appearance of transplants are normal and satisfying. However, FUE costs more than FUT-strip for patients. It also is a much more demanding operation than a strip surgery for surgeons. When the scalp is too tight for a strip excision, FUE is indicated which enables a surgeon to harvest finer hair from the neck. Today, advanced FUE procedures enable the surgeons to gain follicles from different areas such as the abdomen, legs, and chest in a more precise manner.
Which treatment to choose?
During the first session, the surgeon will determine which method best suits the case based on the patient’s expectations, hair loss classification, the size of the thinning area, and the characteristics of the available donor site. Therefore, patients will be able to get realistic and natural looking results.


Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!